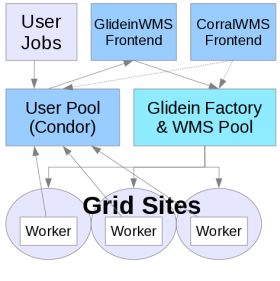
Introduction
Corral is a lightweight frontend for glideinWMS. It is useful for individuals and when running across national cyberinfrastructures such as OSG and TeraGrid. It is also a useful tool when running
Pegasus workflows.Although much work has been done in developing the national cyberinfrastructure in support of science, there is still a gap between the needs of the scientific applications and the capabilities provided by the resources. Leadership-class systems are optimized for highly-parallel, tightly coupled applications. Many scientific applications, however, are composed of a large number of loosely-coupled individual components, many with data and control dependencies. Running these complex, many-step workflows robustly and easily still poses difficulties on today?s cyberinfrastructure. One effective solution that allows applications to efficiently use the current cyberinfrastructure is resource provisioning using Condor glideins.
GlideinWMS was initially developed to meet the needs of the CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) experiment at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. It generalizes a Condor glideIn system developed for CDF (The Collider Detector at Fermilab) and first deployed for production in 2003. It has been in production across the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG), with major contributions from the Open Science Grid (OSG) in support of CMS for the past two years, and has recently been adopted for user analysis. GlideinWMS also is currently being used by the CDF, DZero, and MINOS experiments, and servicing the NEBioGrid and Holland Computing Center communities. GlideinWMS has been used in production with more than 12,000 concurrently running jobs; the CMS use alone totals over 45 million hours.
Corral, a tool developed to complement the Pegasus Workflow Management System was recently built to meet the needs of workflow-based applications running on the TeraGrid. It is being used today by the Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) CyberShake application. In a period of 10 days in May 2009, SCEC used Corral to provision a total of 33,600 cores and used them to execute 50 workflows, each containing approximately 800,000 application tasks, which corresponded to 852,120 individual jobs executed on the TeraGrid Ranger system. The 50-fold reduction from the number of workflow tasks to the number of jobs is due to job-clustering features within Pegasus designed to improve overall performance for workflows with short duration tasks.
The integrated system provides a robust and scalable resource provisioning service that supports a broad set of domain application workflow and workload execution environments. The aim is to integrate and enable these services across local and distributed computing resources, the major national cyberinfrastructure providers (Open Science Grid and TeraGrid), as well as emerging commercial and community cloud environments.
Funded by the National Science Foundation under the OCI SDCI program, grant #0943725